Chlorophyll
Natural greens from leafy plants
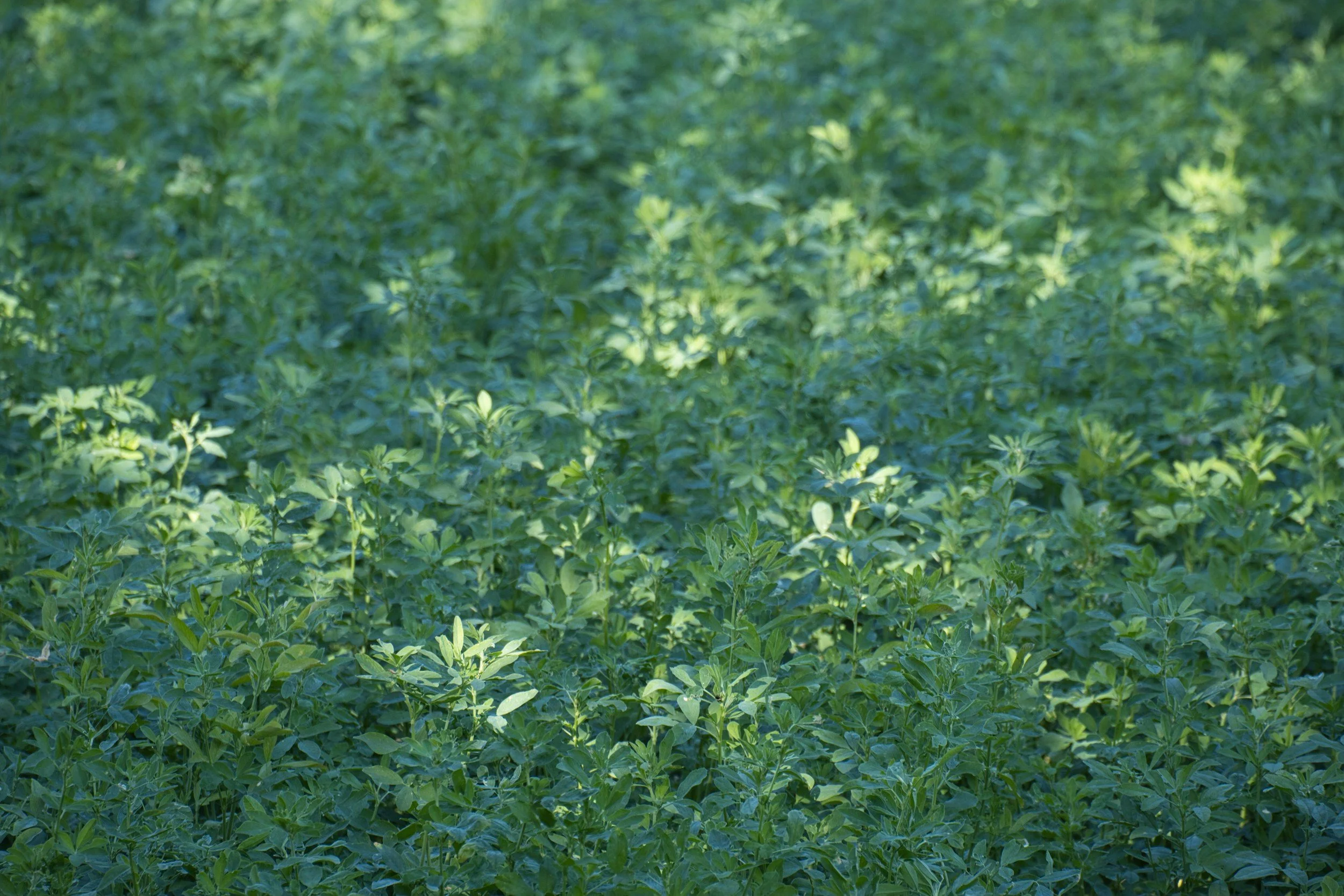
Chlorophyll is sourced from green plant materials such as alfalfa, spinach, or nettle. The leaves are harvested and macerated, then extracted with water or mild solvents to isolate the pigment.
To improve solubility and stability, chlorophyll can be converted into copper chlorophyllin, a water-dispersible form created by replacing the central magnesium ion with copper. This form is more resistant to heat and light and offers improved shelf life. While native chlorophyll is oil-soluble and prone to oxidation, chlorophyllin is more versatile and easier to formulate, especially in neutral pH conditions.
Technical Notes:
pH stability: Chlorophyllins are more stable in alkaline pH; chlorophyll unstable in acid
Light stability: Moderate (better with chlorophyllin)
Heat stability: Chlorophyllins better for heat-treated foods
Solubility:
Chlorophyll: Oil-soluble
Chlorophyllins: Water-soluble
Vegan status: Plant-derived; copper salts permitted in food-grade form
Applications:
Beverages: Herbal drinks, wellness shots, detox juices (mostly chlorophyllin)
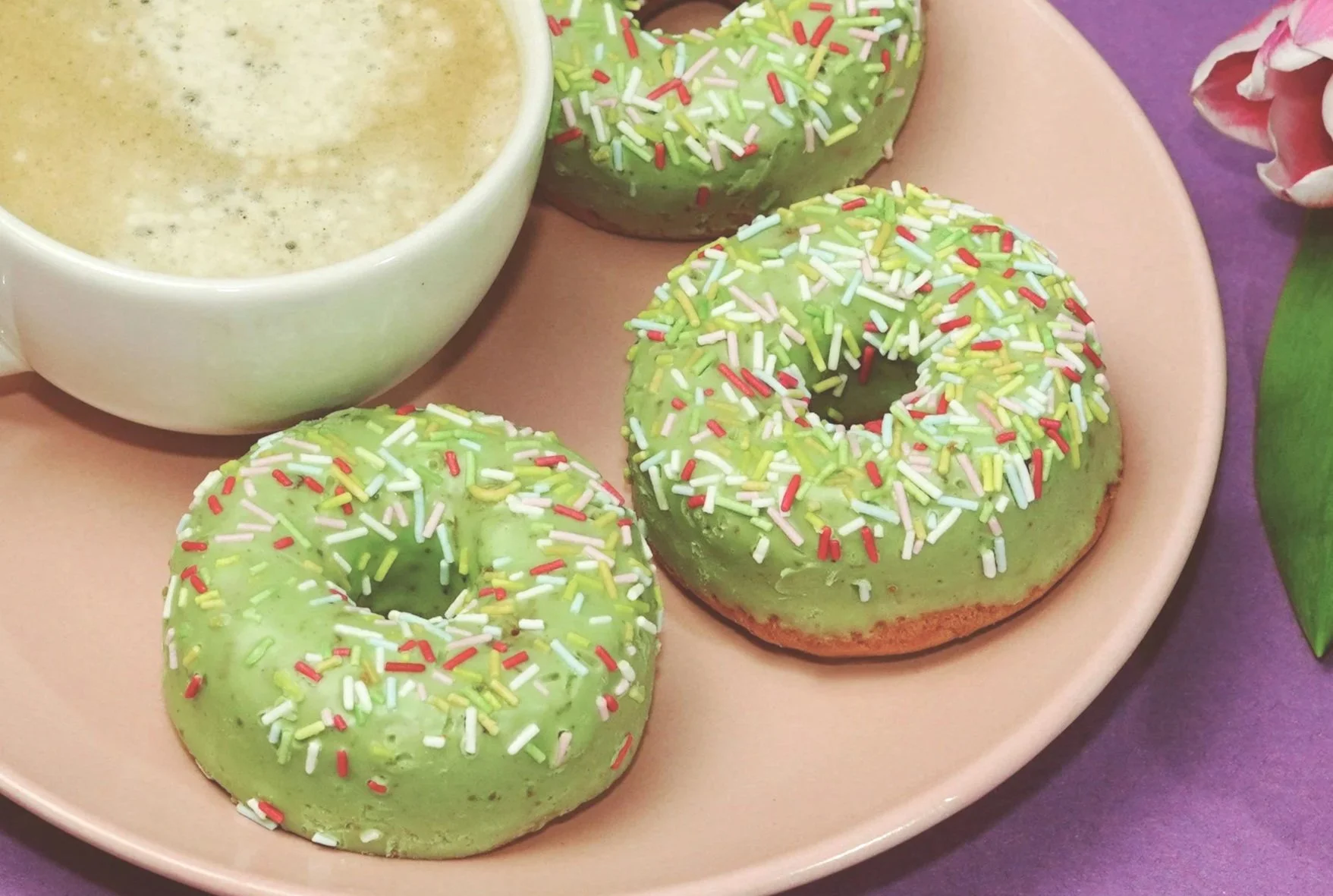
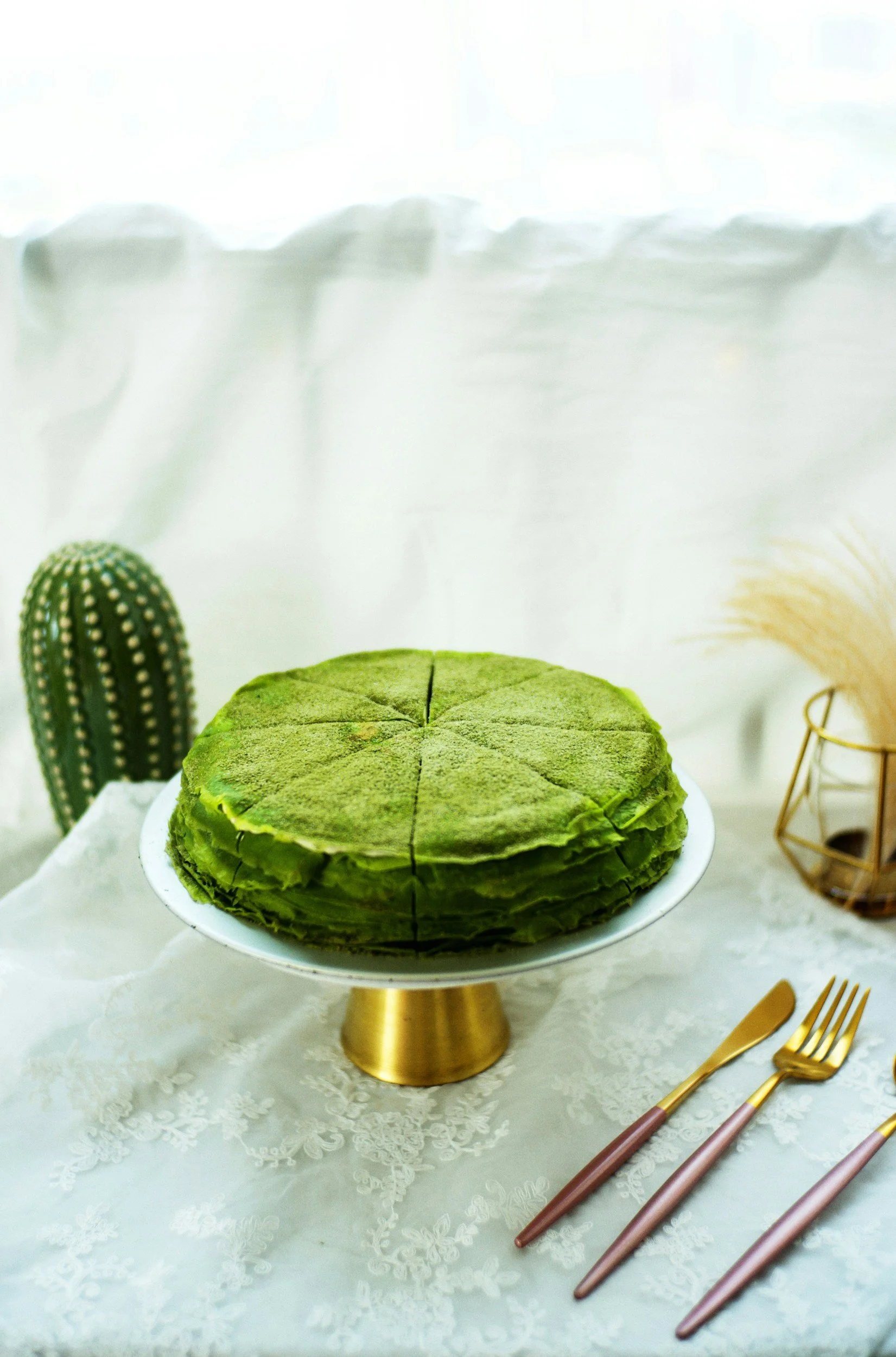
Bakery: Coloured doughs or mint glazes
Confectionery: Mint-flavoured sweets, chewing gum
Savoury: Pesto, green sauces, seasoning blends, fillings
Other: Supplements, health foods, cosmetics