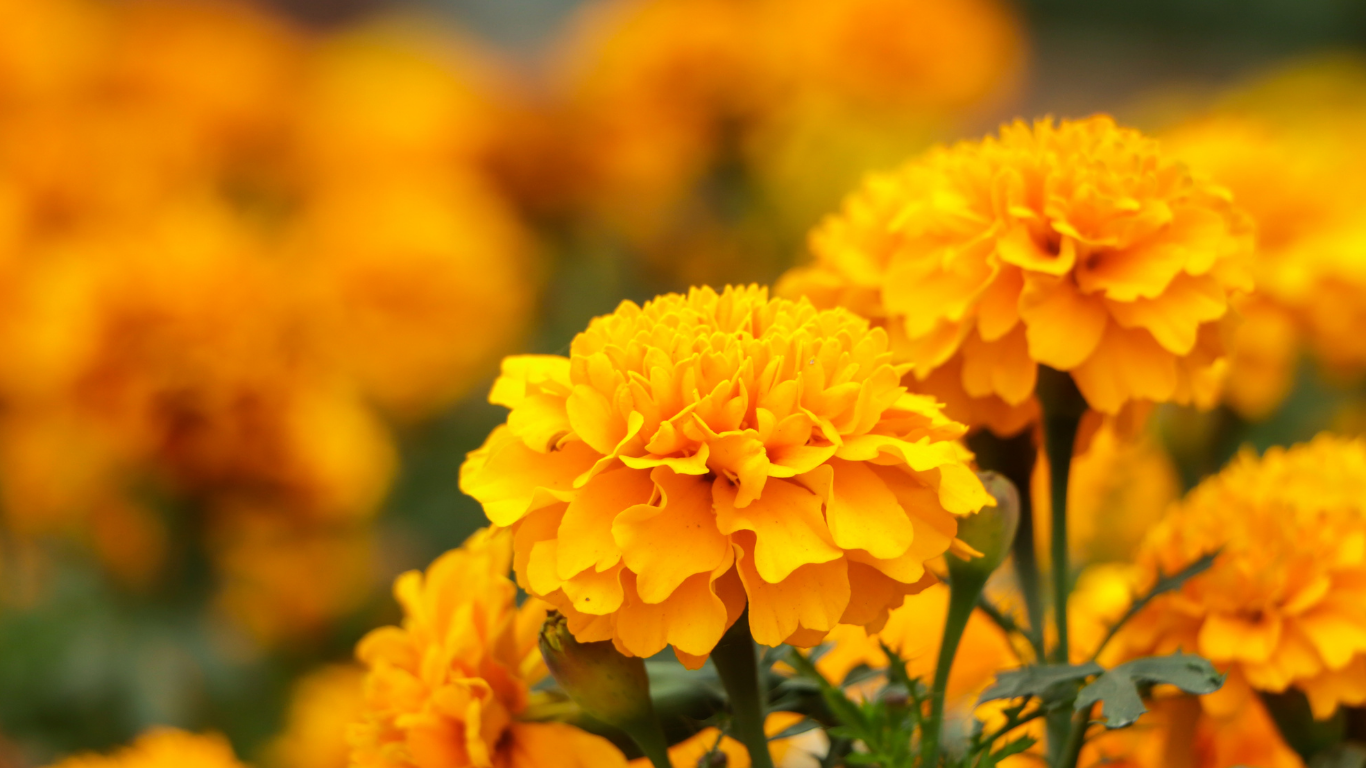
Marigold
Golden yellow from sun-grown blossoms
The marigold plant (Tagetes erecta) produces bright yellow to orange flowers, cultivated mainly in India, China, and parts of South America. The blooms are harvested at full size and then dried to preserve their lutein content—a carotenoid responsible for the golden hue.
Extraction typically involves solvents to isolate lutein in its oil-soluble form, which can later be processed into emulsions or powders for different product types. Maintaining low moisture during drying and controlled temperatures during extraction is essential to preserve the color's strength and purity. Lutein is relatively stable to heat and pH changes, though some sensitivity to oxidation and light remains, especially in clear packaging.
Technical Notes:
pH stability: Good across most pH ranges
Light stability: Moderate
Heat stability: Good in most processes
Solubility: Oil-soluble, emulsions available for water-based systems
Applications:
Beverages: Juices, fortified drinks
Dairy & Ice Cream: Cheese, butter, yogurt
Bakery: Bread, pastries
Confectionery: Candies, fillings
Savoury: Sauces, snacks, pasta products
Other: Supplements, egg yolk enrichment